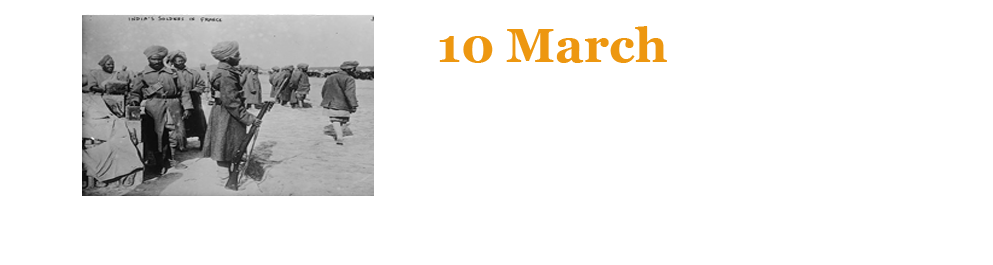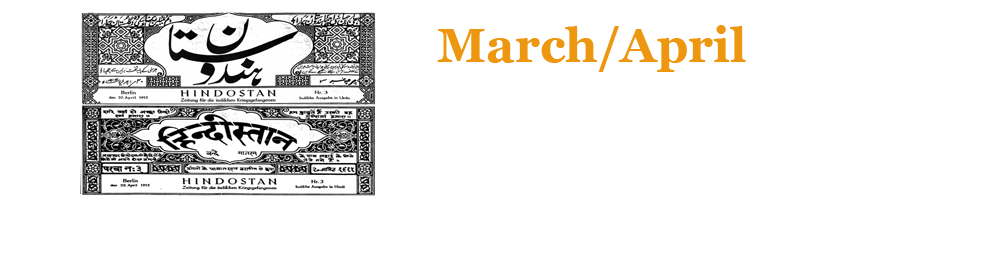Battle of Neuve Chapelle. British and Indian troops undertake their first offensive in France with limited success. Rifleman Gobar Singh Negi, 1/39 Garhwal Rifles wins the Victoria Cross in this action.
Royal Navy warships begin a concerted blockade of Germany and its ports.
British and French warships at the Dardanelles try to force their way through the Narrows. Three ships are sunk; three are badly damaged. Naval operations are suspended.
The First Lahore Conspiracy Case Trial (King Emperor versus Anand Kishore and Others) is held. Ghadar revolutionaries are tried and sentenced to death or long terms of imprisonment.
Hindi and Urdu newsletters are produced for Indian Prisoners of War in Germany. These serve as propaganda for the Germans...

Hindi and Urdu newsletters are produced for Indian Prisoners of War in Germany. These serve as propaganda for the Germans and also feature articles from an Indian nationalistic perspective, including views from the Ghadar movement. These journals were named Hindostan at the request of the Berlin committee and had in its masthead the words ‘Vande Mataram’ and ‘Saare Jahan Se Accha Hindostan Hamara’. Interestingly, British propaganda newspapers targeting Indian troops during the Second World War were titled Hamara Hindustan.
Gen Sir John Nixon lands at Bara and takes command of the British-Indian forces in Mespotamia.
Battle of Shaiba. Turkish forces defeated. Their commander, Suleiman Askeri, commits suicide.
Second Battle of Ypres. Germans launch major assault on French, British, Indian and Canadian troops around Ypres and use poison gas extensively for the first time. Fighting continues until 27 May.
Battle of St. Julien. Germans attack Canadian part of Ypres Salient. The British and Indian troops counter-attack to recapture lost ground.
First landing at Gallipoli. British, Indian, French, Australian and New Zealand troops land on and around the Gallipoli peninsula in support of the naval attack on the Dardanelles. Fighting continues until January 1916.
Battle of Helles in Gallipoli.
Jemadar Mir Dast, 55th Coke's Rifles leads his men with great bravery during the attack at Wieltje, Belgium. He is awarded the Victoria Cross.
Battle of Aubers Ridge. To support French operations in Artois, British and Indian troops attack in French Flanders but achieve no real gains. Battle continues until 10 May.
First Battle of Krithia in Gallipoli.
Battle of Festubert. British and Indian troops undertake another attack in French Flanders only a short distance from Aubers Ridge. Battle carries on until 25 May.
Defence of Anzac. At Gallipoli, Australian, New Zealand and Indian troops fight off a very heavy Turkish attack. After weeks of effort on both sides, it is clear stalemate has been reached.
Italy declares war on Austria-Hungary and moves to secure strategically important points along their shared border.
Second landing at Gallipoli. After all attempts to move inland have been defeated, a new British and Indian landing is made at Suvla Bay, linked to an assault on the hills beyond the Australian and New Zealand position. The operations fail.
Battle of Sari Bair in Gallipoli.
Battle of Scimitar Hill.
"Berlin Committee (later the Indian Independence committee) promoting the cause of Indian independence during the First World War is formed. Notable members include Virendranath Chattopadhyay (Chatto)....

"Berlin Committee (later the Indian Independence committee) promoting the cause of Indian independence during the First World War is formed. Notable members include Virendranath Chattopadhyay (Chatto), Abhinash Chandra Bhattacharya, Tarachand Roy. This organisation collaborated extensively with the German Foreign Office and was thus cited as being part of the ‘Hindu-German conspiracy'. The ‘Hindu-German conspiracy’ refers to a series of activities organised by Indian revolutionaries, with varying degrees of support from Germany, to utilize the backdrop of the War to weaken and overthrow the British Empire. These events include the Christmas Day Plot of 1915, the Annie Larsen Affair in the US, the activities of the Berlin Indian Independence Committee among others."
Co-ordinated Allied offensive in France, with French attacks in the Second Battle of Champagne and Third Battle of Artois, and British and Indian attacks at the Battle of Loos. The fighting at Loos carries on until 4 November.
Rifleman Kulbir Thapa, 3rd Gurkha Rifles, is awarded the Victoria Cross. Having been wounded himself, he found a wounded soldier of The Leicestershire Regiment behind the first line German trench. Although urged to save himself, the Gurkha stayed with the wounded man all day and night...

Rifleman Kulbir Thapa, 3rd Gurkha Rifles, is awarded the Victoria Cross. Having been wounded himself, he found a wounded soldier of The Leicestershire Regiment behind the first line German trench. Although urged to save himself, the Gurkha stayed with the wounded man all day and night. Early next day, in misty weather, he took him through the German wire and, leaving him in a place of comparative safety, returned and brought in two wounded Gurkhas, one after the other. He then went back, and, in broad daylight, fetched the British soldier, carrying him most of the way under enemy fire.
Battle of Kut Al Amara.
British and French troops land in the Greek city of Salonika to support Serbia, by threatening the southern flank of Bulgaria.
General Sir Ian Hamilton is replaced in command at Gallipoli by General Sir Charles Monro.
The Niedermayer-Hentig expedition organised by the German foreign office and headed by the Bavarian officer Oscar Niedermayer, a Prussian diplomat Werner-Otto von Hentig....

The Niedermayer-Hentig expedition organised by the German foreign office and headed by the Bavarian officer Oscar Niedermayer, a Prussian diplomat Werner-Otto von Hentig and the exiled Indian prince Mahendra Pratap reaches Kabul. This mission sought to convince the Emir of Afghanistan to join the Central Powers and allow troops to attack British India through Afghan territory. The Berlin Committee was involved in consultations regarding this mission, for which Indian PoWs from prison camps in Germany were also recruited. These efforts were ultimately futile.
Indian infantry begins to leave France in order to transfer to Mesopotamia.
Battle of Ctesiphon. In Mesopotamia, Turkish forces stop the Anglo-Indian advance on Baghdad only 40 km (25 miles) south of the city. Maj Gen Townshend falls back on Kut Al Amara.
The provisional Government of India in exile is formed in Kabul headed by Raja Mahendra Pratap, Ubaidullah Sindhi, Champakaraman Pillai and Maulana Barkatullah. At the time, Sindhi was working....

The provisional Government of India in exile is formed in Kabul headed by Raja Mahendra Pratap, Ubaidullah Sindhi, Champakaraman Pillai and Maulana Barkatullah. At the time, Sindhi was working with what has come to be known as the ‘Silk Letter Movement’, while Pillai and Barakatullah were involved with the Berlin committee. This government in exile was disbanded in 1918, following British pressure on Afghanistan.
Siege of Kut begins. After their defeat at Ctesiphon, Anglo-Indian troops fall back on Kut Al Amara where they are surrounded by Turkish forces. They eventually surrender on 29 April 1916.
General Sir Douglas Haig replaces Field Marshal Sir John French as Commander in Chief of the British Expeditionary Force in France and Belgium.
Troops evacuated from the Suvla and Anzac beachheads at Gallipoli.
‘The Christmas Day Plot’, a planned uprising in Bengal by the revolutionary organisation Jugantar with the help of German arms, in coordination with the Ghadar party’s plan to initiate uprisings in Burma and Siam. This plan is thwarted by British intelligence.